With the increasing incidence of lung cancer yearly, people’s concern over lung cancer prevention should be aroused. Therefore, being well informed of the causes of lung cancer is essential. After decades of research conducted in this field, scientists find out that besides the main cause smoking, lung cancer also attributes to the following factors:
Passive smoking
Passive smoking or long-term breath in tobacco smoke from other smokers sharing living or working space is also an established risk factor for the development of lung cancer. Research has shown that nonsmokers who live with a smoker have a 24% increase in risk for developing lung cancer.
Asbestos fibers
Asbestos fibers are silicate fibers that can remain in lung tissue for lifetime. As asbestos was widely used for materials in the workplace, it’s a common source of exposure to asbestos fibers. So asbestos use is limited or banned in many countries now. Exposed workers who smokes are tend to have higher risk of developing asbestos-related lung cancer.
Radon gas
Radon gas is a natural, chemically inert gas that is a natural decay product of uranium. It decays to form products that emit a type of ionizing radiation. Radon gas is a known as cause of lung cancer, with an estimated 12% of lung cancer deaths attributable to radon gas. Along with asbestos exposure and smoking, radon exposure can greatly increases the risk of lung cancer. Familial predisposition
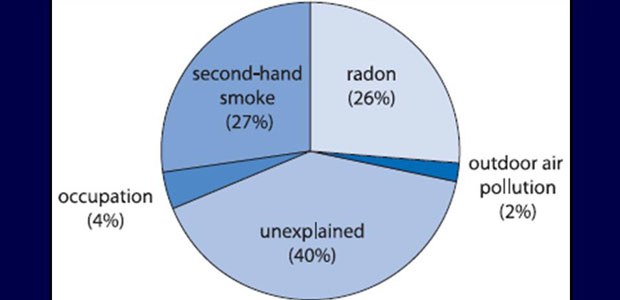
Tobacco smoking cause the majority of lung cancer, but there’re also other factors such as individual genetic susceptibility, which may play a role in the causation of lung cancer. Numerous studies have shown that lung cancer is more likely to occur in both smoking and nonsmoking relatives of those who have had lung cancer.
Prior history of lung cancer
Survivors of lung cancer have a greater risk than the general population of developing a second lung cancer. Survivors of non-small cell lung cancers have an added risk of 1%-2% per year for developing a second lung cancer. In survivors of small cell lung cancers, the risk for development of second cancers approaches 6% per year.
Lung disease
Certain lung disease, especially chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , is closely connected to a slightly increased risk for the development of lung cancer even exclude the effects of cigarette smoking.
Air pollution
Air pollution, from vehicles, industry, and power plants can raise the chance of developing lung cancer. Up to 1% of lung cancer deaths are attributable to breathing polluted air, and experts believe that prolonged exposure to highly polluted air can carry a risk similar to that of passive smoking for the development of lung cancer.
Knowing all these causes of lung cancer greatly contributes to cancer prevention. Oncologists from St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou remind that keep an eye out for these threatening factors.
*Surgery, in addition to the appropriate chemotherapy and radiotherapy, are effective in treating early cancer, but certain patients in late stage of cancer may not be tolerate surgery well as they can be relatively weak. A combination of carefully planned minimally invasive therapy, chemotherapy or radiotherapy can effectively reduce the side effects and discomfort of treatment and may help patient get better efficacy.













 viber
viber