Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas. The abnormal cells do not develop into healthy lung tissue, they divide rapidly and form tumors. And lung cancer can be divided into the following stages:
Stage 0: This is called in situ disease, meaning the cancer is “in place” and has not grown into nearby tissues and spread outside the lung.
Stage I: A stage I lung cancer is a small tumor that has not spread to any lymph nodes, making it possible for a surgeon to completely remove it. Stage I is divided into 2 substages based on the size of the tumor. Stage IA are less than 3 centimeters wide. While stage IB tumors are more than 3cm but less than 5cm wide.
Stage II: Stage II lung cancer is divided into 2 substages:
Stage IIA cancer describes a tumor larger than 5 cm but less than 7cm wide that has not spread to the nearby lymph nodes. Or a stage IIA cancer can be a small tumor less than 5 cm wide that has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
Stage IIB lung cancer describes a tumor larger than 5 cm but less than 7 cm wide that has spread to the lymph nodes. Sometimes stage II tumors can be removed with surgery, and other times, more treatments are needed.
Stage III: Stage III lung cancers are classified as either stage IIIA or stage IIIB. For many stage IIIA cancers and nearly all stage IIIB cancers, the tumor is difficult, and sometimes impossible, to remove. For example, the lung cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes located in the center of the chest, which is outside the lung. Or, the tumor may have grown into nearby structures in the lung. In either situation, it is less likely that the surgeon can completely remove the cancer because removal of the cancer must be performed bit by bit.
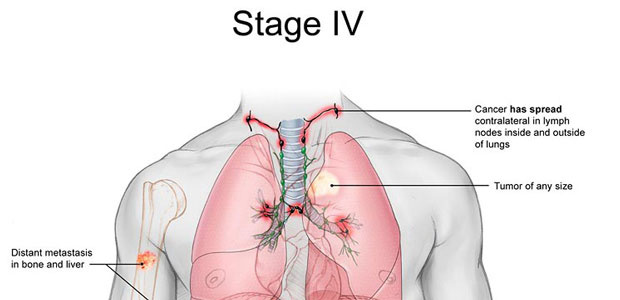
Stage IV means the lung cancer has spread to more than 1 area in the other lung, the fluid surrounding the lung or the heart, or distant parts pf the body through the bloodstream. Once cancer cells get into the blood, the cancer can spread to anywhere in the body. But, NSCLC is more likely to spread to the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal glands. Stage IV NSCLC is divided into 2 substages.
Stage IVA cancer has spread within the chest.
Stage IVB has spread outside of the chest.
In general, surgery is not successful for most stage III or IV lung cancers. Lung cancer can also be impossible to remove if it has spread to the lymph nodes above the collarbone or vital structures within the chest, which include the heart, large blood vessels, or the main breathing tubes leading to the lungs. In these situations, the doctors from St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou recommend other minimally invasive treatment options such as interventional theray, crotherapy, nanoknife, particle implantation and TCM & western medicine, etc.
*Surgery, in addition to the appropriate chemotherapy and radiotherapy, are effective in treating early cancer, but certain patients in late stage of cancer may not be tolerate surgery well as they can be relatively weak. A combination of carefully planned minimally invasive therapy, chemotherapy or radiotherapy can effectively reduce the side effects and discomfort of treatment and may help patient get better efficacy.













 viber
viber