- Basic
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatments
What is soft tissue cancer?
All malignant tumors that originate in the fiber, fat, smooth muscle, striated muscle, synovial membrane, blood vessel, lymphatic vessel and locate in soft tissues (with the exception of visceral organs), are called as soft tissue cancers or soft tissue sarcomas as well. Sarcoma can occur in the soft tissues throughout the body, especially in the limbs, trunk, retroperitoneal part and pate; among these, the limbs are mostly seen, about 60% in all cases. The incidence rate of soft tissue cancer is approximately 2/100,000 to 3/100,000, which amounts for 1% among adult’s malignant tumors, but it has no sexual orientation. Generally the elderly have a higher prevalence. Soft tissue cancer is very easy to spread to the surrounding normal tissue and its fatality rate is 2%.
Survival rate of soft tissue cancer
Prognosis of soft tissue cancer patients is better than that of epithelium tumor patients and its 5-year survival rate is about 50%. Prognosis mainly depends on tumor’s condition and invasion severity of adjacent organs, and the prognosis of limbs is prior to other parts. For patients who have occurred metastasis but treatments still can control the condition, the survival rate for most of these patients after being diagnosed with metastasis is about 1 year.
Causes of soft tissue cancer:
Currently, causes of soft tissue cancer have not been defined yet, but it is well-known that the causes of soft tissue cancer are not single.
1. congenital malformation: angeioma is commonly seen among infants and children. The vast majority of such lesions are found after birth. As children grow, vascular lesions will grow correspondingly and proportionally and never fade away without rapid growth history.
2. Familial heredity: many studies show that many tumor cells manifest chromosomal abnormalities. People who have chromosomal abnormalities would own higher incidence rate than that of normal people, and also have the characteristic of familial heredity.
3. Foreign substance stimulation: according to animal experiment and clinical observation, long term of foreign substance stimulation on the body may induce soft tissue cancer.
4. Chemical materials stimulation: an epidemiological survey has discovered that workers who are long-term exposed to polyvinyl chloride have high risk of suffering from angiosarcoma of the liver
5. Trauma: a considerable portion of soft tissue cancer patients have clear trauma history on the site of tumor.
Risk of Soft Tissue Cancer
Soft tissue cancer usually grows rapidly with huge volume, invades and damages surrounding normal tissues. The tumor itself may have necrosis, bleeding and secondary infection, and often spreads to the lung, bone, skin, brain, adrenal, pancreas and other organs by hematogenous dissemination. Patients often die of cachexia, severe bleeding or widespread metastasis.
Staging of Soft Tissue Cancer
Tumor staging depends on the size of the tumor, pathological grading and whether there is a nearby lymph nodes metastasis or distant metastasis.
Soft tissue cancer of adults shall be divided into 4 stages: Stage I, II, III means there is no nearby lymph nodes metastasis or distant metastasis. During Stage IV, if there is regional lymph nodes metastasis, then it is Stage Iva; if there is distant metastasis, then it is Stage IVb.
Pathological grading mainly depends on tumorous mitotic values. The first grading: division of tumor cells is slow and metastases seldom occur; the second grading: tumor cells have moderately differentiated with the probability of metastasis being less than 20%; the third grading: division of tumor cells is relatively quick with the probability of metastasis being exceeding 50%.
5-year survival rate for people with low differentiated tumor usually exceeds 75%; while for people with high differentiated tumor, it is less than 25%.
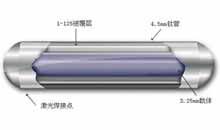
Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou has created the “super minimally-invasive targeted diagnosis and treatment system” on the basis of interventional embolization, radioactive particles implantation, biological immunotherapy, cryotherapy. In addition to the above advantages, the system can local- directionally kill tumor without damage to the surrounding normal tissues and organs, so as to avoid to destruct patients’ immunities because traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy often damage other normal soft tissues and also eliminate excessive treatment. Treatment of traditional Chinese medicine has Chinese characteristics as Chinese culture has a long history of China for thousands of years; dialectical therapy of traditional Chinese medicine can regulate the balance, strengthen body resistance and enhance anticancer effect, so that further alleviate the symptoms and prolong the survival time. Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou combine minimally-invasive targeted therapy with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine to give full play of the advantages of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine, and to use new treatment system to achieve the best therapeutic effect and reduce the suffering of patients, which greatly extend the survival time of the patients, improve the quality of life and long term therapeutic effects.
Soft tissue tumors are tumors that occur in mesenchymal tissue, including epidermal and dermal benign tumor, cystic lesion, and malignant tumor located in the deep fascia. Most of the soft tissue tumors are benign tumors; manifestations of benign and malignant tumors are similar. Whatever malignant tumors that happened in the soft tissue, in principle are called sarcoma.
Causes of soft tissue tumor
Currently, causes of soft tissue tumor have not been defined yet, but it is well-known that soft tissue tumor is related to the following factors: 1. Gene (genetic) theory: gene mutations of normal cells can cause cancer. Tumor cells constantly proliferate and inherit the biological characteristics, such as hereditary multiple exostosis. 2. Chronic stimulation theory: (1) chemical chronic stimulation, (2) physical factors. 3 Virus theory has found that blood serum of patients with osteosarcoma contain specific antibodies of osteosarcoma. 4. canceration.
Symptoms of soft tissue tumor
1. Systemic manifestation: both benign tumor patients and early malignant tumor patients rarely have obvious systemic symptoms. Late malignant tumor patients, such as bone sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma or metastatic carcinoma, can have cachexia symtoms, such as anaemia, emaciation, loss of appetite, weight loss, fever, etc.
2. Local manifestation: pain of bones, joints, soft tissue, osseous or soft tissue mass, dysfunction, these are common local manifestations of malignant bone tumors.
(1) Pain: pain is the most common symptom of tumors of rapid growth. At the beginning, the pain is light and intermittent, and gradually develops into a violent persistent pain. This is mainly due to tension or pressure imposed by bone tumor to sensitive periosteum or endosteum. But the pain does not necessarily explain the tumor is malignant, because some benign tumors, such as osteoid osteoma may cause pain due to reactive bone growth and pain. If pain suddenly and violently attacks, this may easily cause pathological fracture.
(2) Mass: benign tumors often present hard and non-tender lumps. Malignant tumors of rapid growth often present as a diffuse swelling, tenderness, skin fever, superficial venous engorgement.
(3) Dysfunction and compression: if tumor is close to joint, activities will be restricted; pain would increase when the joint moves. For tumors occurred in spinals, no matter benign or malignant, spinal cord compression would be caused and further lead to paralysis.
(4) Malformations: patients in growth age or patients with pathological fractures, may suffer from malformation, for instance, multiple osteochondroma would affect growth, and even cause limb bending with unequal lengths. Enchondroma can make bonelets of hand and foot deformed. If tumor invades into epiphyseal plate, then it would cause maldevelopment.
Experts of Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou remind: the above symptoms are common symptoms of soft tissue tumor, if similar circumstances occur, patients should go to standardized hospital a.s.a.p. for examination or treatment.
Early soft tissue tumors have few obvious systemic symptoms, while advanced malignant soft tissue tumors may cause symptoms like fever, anemia, loss of appetite, weight loss. It is not difficult to distinguish between malignant and benign soft tissue tumors. Based on the patient’s clinical situation and history and combined with the following inspection methods, soft tissue tumors can be detected:
1. X -ray examination: X -ray is helpful in further understanding the range and transparency of soft tissue tumor and its relationship with nearby sclerotin. The clear boundary often suggests benign tumors while clear boundary with calcifications often suggests malignant soft tissue tumors, which are often seen in synovial sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, and so on.
2. Ultrasound imaging examination: it can reveal the range and envelope boundary of the tumor, as well as the echo of internal tumor tissues, so as to distinguish whether it is benign or malignant. Malignant soft tissue tumor has big body, unclear boundary, and vague echo, which usually occur in rhabdomyosarcoma, synovial myosarcoma, malignant fibrohistiocytoma, etc. Ultrasound can also guide acupuncture aspiration cytology examination for deep tumors.
3. CT examination: as CT can identify the density and space of soft tissue tumor, it is a commonly used method to diagnose soft tissue tumor in recent years.
4. MRI examination: it can make up the shortcoming of X-ray in diagnosing soft tissue tumors. It can reveal all the layers of the tissues and the range of the tumor with a longitudinal section. It provides even clearer images of retroperitoneal soft tissue tumors, tumors spreading to the butt or thigh from pelvis and tumors in the popliteal fossa, as well as tumor infiltration to bone or bone marrow. It is a good basis to settle the treatment plan.
5. Pathological examination
(1) Cytological examination: it is a simple, quick and accurate pathological examination method. It is most suitable for following situations:
a. Ulcerated soft tissue tumors: microscopy on smear or scraping of the sample.
b. soft tissue tumor with pleural fluid or ascites: centrifugalize and enrich the fresh sample and then make the smear
c. acupuncture aspiration smear is suitable for tumors that have big body, situate in deep area and to be treated with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, as well as transferred and recurrent lesion.
(2) Protractor biopsy: it can be used when ulceration has happened to the soft tissue tumor and cytological smear can not diagnose the tumor.
(3) Incisional biopsy: it is mainly used in surgery.
(4) Excisional biopsy: it is suitable for small soft tissue tumors. The normal tissues surrounding the tumor can also be taken for pathological examination.
As the tissue source of soft tissue tumor are complicated and various, apart from common HE staining, most diagnoses of the tumors require assistance of immunohistochemistry or electron microscope during pathological examination.
Experts from Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou remind that: soft tissue tumors can get a better treatment effect with early detection and treatment. Therefore, once any discomfort happens, one should go to regular hospital for examination and treatment as soon as possible.
Soft tissue tumors are clinically common, and the origins of the tumor tissue origin are complex with multiple types, but the treatment principles are basically identical, hereby we would like to introduce the following treatment methods:
Surgery of soft tissue tumor
1. Radical operation: tumors together with the surrounding normal tissue must be removed at the same time, in order to ensure complete resection, often some normal tissue structures, parts, skins or adjacent partial muscles are also removed; 2 debulking operation; 3. amputation.
Radiotherapy of soft tissue tumor
Complete radical operation can cause functional injury, amputation or joint disarticulation, so another choice is combined application of operation and radiotherapy. After operation, radiotherapy can be applied to pay the inhibition role for tiny subclinical lesions remained within the operation field, but it is ineffective to those large tumors in lump-like or in nodular shape.
Chemotherapy of soft tissue tumor
1. Chemotherapy prior to operation: for those soft tissue tumors of large volume and in high malignancy, preoperative chemotherapy is preferred to decrease the volume and increase the resection rate so that avoid suffered amputation.
2. Chemotherapy after operation: surgery combined with chemotherapy, has been widely used in the clinical treatments of various malignant tumors. In the treatment of highly malignant soft tissue sarcomas, chemotherapy should be begun to use shortly after operation. It is possible to reduce distant metastasis and improve the survival rate.
Gene targeted therapy
Gene targeted therapy, is targeted at clearly-defined carcinogenic site (the site may be a protein molecule or a genetic fragment inside of tumor cells) and then to design corresponding treatment drugs. The drugs will specifically select and work on the carcinogenic sites to bring death to tumor-specific cells without affection to surrounding normal tissue cells. Simply say, it first correctly seeks the tumor target——a gene, and then destroy it. Or let’s say, it precisely targets at key carcinogenic site of cancer cell growth (such as enzymes, proteins, receptors, etc.), and then launches a guided “missile" to destroy growth of cancer cells.
Experts from Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou would choose the best treatment plan based on patient’s own condition to improve his/her life quality and prolong the survival period.
If you have any questions, please contact us via online consultation, email or phone call. If you find our website useful, please follow our FaceBook and YouTube, health information will be updated regularly.